Table of Contents
ПереключатьOverview of NFC Data Transmission
НФК, a low data rate and short-range wireless communication technology, operates through a synergy of two devices—termed as the initiator and the target. Commonly recognized as the tag and reader, these entities engage in data exchange via an RF carrier frequency of 13.56 MHz, relying on contactless electromagnetic induction. The requisite proximity for such interactions is typically less than 10 cm.
Standards & Communication Protocols in NFC
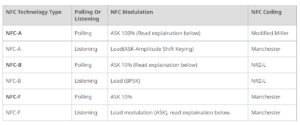
Based on varying data rates, along with distinct modulation and coding requirements, NFC technology is manifested through three principal standards: NFC-A, NFC-B, and NFC-F. These standards are associated with different modulation and encoding types, as illustrated in Table-1.
NFC Non-Return-to-Zero Level (NRZ-L) Encoding
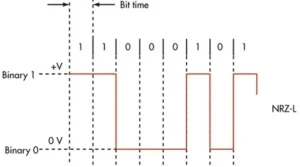
- Representation: The NRZ-L encoding schematic is depicted in Figure-1, where a binary ‘1’ is signified by a high voltage (+V), and a binary ‘0’ is denoted by a low voltage (0 volt).
- Characteristic: Also dubbed as unipolar NRZ coding, this representation is straightforward, marking each bit value with a distinct voltage level.
NFC Manchester Encoding
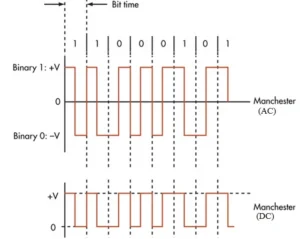
- Variation: Two variants of Manchester codes exist—AC (bipolar) and DC (unipolar) types.
- Transition Significance: Both binary ‘1’ and ‘0’ are characterized by voltage transitions within the same bit period—High-to-Low signifies a binary ‘1’, while Low-to-High implies a binary ‘0’.
- Transition Precision: These transitions are meticulously placed at the midpoint of the bit period, reinforcing the clarity of data signals.
NFC Modified Miller Encoding
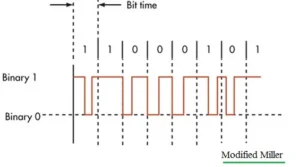
- Binary ‘1’ Mapping: Binary logic ‘1’ is invariably indicated by a transition from high to low and then back to high within the bit period, irrespective of the previous bit’s state.
- Binary ‘0’ Mapping: The portrayal of binary ‘0’ is contingent on the preceding bit’s condition—If the previous bit was a ‘1’, current zero follows a reverse transition pattern, and if it was a ‘0’, the mapping echoes that of a binary ‘1’.
Types of Modulation in NFC
NFC embraces a range of modulation types such as Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) in both 10% and 100% variants and employs load modulation techniques. These modulation methods are integral to the precision and efficiency of NFC communication protocols.
In Summary
NFC’s architecture is predicated on sophisticated modulation and coding protocols, with each standard employing unique mechanisms to ensure secure and effective communication between near-proximity devices. Whether through NRZ-L’s voltage levels, Manchester’s transition-based binary indications, or Modified Miller’s context-dependent mappings, NFC technology demonstrates adaptability to a multitude of operational environments and needs.
Джеки
Опытный эксперт IoT с большим опытом разработки и развертывания взаимосвязанных систем, которые позволяют использовать интеллектуальные и эффективные технологии в различных отраслях. Мои навыки в решениях IoT вносят значительный вклад в развитие связанных сред.
